CERN Scientific Committees
When the proposal for an experiment at CERN is sufficiently advanced, generally after long discussions between many people, and an assessment has been made of the financial implications of the project, the time required on one or other of the machines, and the necessary experimental equipment and staff, it is submitted to the appropriate CERN Scientific Committee.
These committees also make recommendations on the facilities offered by the accelerators in their respective fields.
The committees' proposals and recommendations were passed on to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee from 1960 to 1976 and to the Research Board from 1976 to today for the final decisions concerning the experimental programme and the facilities offered by the accelerators.
Information about current and former committees (in alphabetical order) is given below:
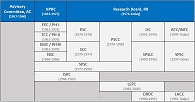
AC | DRDC (1) | DRDC (2) | EEC | EmC | INTC | ISC | ISRC | ISTC | LEPC | LHCC | NPRC | NSC | PH-I | PH-II | PH-III | PSC | PSCC | RB | SCC | SPSC (1) | SPSC (2) | SPSLC | TCC
Advisory Committee (AC), 1957 - 1960 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
During a meeting of the Scientific Policy Committee, it was decided to propose to the Council the creation of an Advisory Committe to advise the Director-General on matters concerning the utilization of the accelerators by visiting teams from Member States. The Advisory Committee was established in June 1957. It met for the first time in August 1957 in the presence of seven visitors' representatives and ten CERN staff, when it discussed their proposals for Synchro-Cyclotron (SC) experiments. The committee met six times between 1957 and 1960. With the Proton Synchroton (PS) commissionnned in November 1959, a global policy was defined for the exploitation of the SC and the PS. The Advisory Committee (for the SC, PS and Emulsion techniques) was taken over by three new experimental committees, one for each experimental technique used: the Electronic Experiments Committee (EEC), the Track Chamber Committee (TCC) (for the Bubble Chambers) and the Emulsion Committee.
|
||||||
Detector Research and Development Committee (DRDC-1), 1990 - 1995 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Detector Research and Development Committee (DRDC) was set up in July 1990. It received proposals for detector R&D involving people from Member States, other countries, and CERN itself. The committee operated in the same way as the other experimental committees of CERN, and forwarded its recommendations to the Research Board for final decision. It held its last meeting in January 1995. Its role was taken over by the LHC Committee (LHCC) and SPS Committee (SPSC).
|
||||||
Detector Research and Development Committee (DRDC-2), 2023- Present |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
Electronic Experiments Committee (EEC) - Physics I Committee (PH-I-COM), 1961 - 1976 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1960 the Director-General John Adams proposed a number of measures to define a global policy for the exploitation of the Synchro-Cyclotron (SC) and the new Proton Synchrotron (PS). He decided to create three Committees, one for each experimental technique used:
These three new committees were proposed to replace the Advisory Committee and the Bubble Chamber Committee. The EEC had the task of examining proposals for electronics experiments (counter and other electronic experiments not included in the TCC and EmC functions) to be carried out at the CERN 28GeV Proton Synchrotron (PS), and making recommendations to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC). It formed a link between the European counter groups and the CERN Laboratory. The EEC came into operation in 1961, and met about once a month. The first meeting was held on 1 March, 1961. It comprised a Chairperson (a senior physicist working on electronic experiments, not on the staff of CERN) and Members (representatives of CERN and other European counter groups wanting to use the CERN facilities).
In 1966, the EEC was often called the Physics I Committee (PH-I-COM). This name referred to the new departments, Physics I and Physics II, which had just been created as an additional layer in CERN's organisational structure. The name PH-I was sometimes used (from 1966 until the departments were abolished in 1976) in the numbering systems of EEC. For example, propositions for the EEC were given "PH-I-COM-YY-RN" numbers, while EEC minutes had "EEC-YY-RN" numbers.
In 1976 (end of the bubble chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental techniques, and basing it instead on the machine. EEC and TCC merged to become the Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC).
Source : CERN-344-Rev.4 ; CERN Courier, Vol.7, N°3
Lists of PH-I-COM documents: 1966 to 1972 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Emulsion Experiment Committee (EmC) - Physics III Committee (PH-III-COM), 1961 - 1976 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1960 the Director-General John Adams proposed a number of measures to define a global policy for the exploitation of the Synchro-Cyclotron and the new Proton Synchrotron. He decided to create three Committees, one for each experimental technique used:
These three new committees were proposed to replace the Advisory Committee and Bubble Chamber Committee.
The EmC's functions were to propose to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee emulsion experiments to be carried out at CERN, and also to form a link between the European emulsion groups and the CERN Laboratory.
The EmC came into operation in 1961, and met about once a month. It comprised a Chairperson (a senior physicist working on emulsion experiments, not on the staff of CERN) and members (representatives of CERN and other European emulsion groups wanting to use CERN facilities).
In 1966 the importance of emulsion techniques decreased rapidly, and following a proposal by B. Gregory, G. Ekspong and L. Van Hove, it was decided to merge the EmC with the Nuclear Structure Committee (NSC) to form the Physics III-Committee (PH-III-COM).
In 1976 (end of the bubble chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental technique, and basing it instead on the machine. PH-III Committee became the SC Committee (SCC), which existed until 1978.
Source : CERN-344-Rev.4 ; CERN Courier, Vol.7, N°3
Lists of PH-III documents : 06/1966 to 05/1968 | 05/1968 to 12/1968 | 01/1969 to 05/1969 | 05/1969 to 02/1970 | 1970 | 1971 | 1972 | 1973 | 1974 | 01/1975 to 08/1975 | 09/1975 to 12/1975 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ISOLDE Committee (ISC), 1991 - 1999 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Isolde Committee (ISC) was set up in 1991 to evaluate proposals for experiments on the Isolde facility (On-Line-Isotope Separator) after its transfer to the Proton Synchrotron (PS) Booster. The ISC held four meetings per year. The committee's conclusions were transmitted to the Research Board (RB) by the Chairperson. Previously, Isolde had operated on the Synchro-Cyclotron (approved by the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC) on 17 December 1964). In 1999 ISC became Isolde and Neutron Time-of-Flight Experiments Committee (ISTC), evaluating proposals for experiments of Isolde facility and in addition for the Neutron Time of Flight facility.
|
|||||||||
ISOLDE and Neutron Time-of-Flight Experiments Committee (ISTC), 1999 - (INTC), 2000 - Today |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Isolde and Neutron Time-of-Flight Experiments Committee (ISTC) was set up in 1999 and the abbreviation was changed to INTC in 2000. It took over the duties of evaluating proposals for experiments on the ISOLDE facility that was formerly in the hands of the Isolde Committee (ISC). In addition it reviews experiments proposed for the Neutron Time of Flight (nTOF) facility which started operating in 2000. The INTC works on a basis of four meetings per year. The committee's conclusions and recommendations are transmitted to the Research Board (RB) by the Chairperson for the final decisions, in particular on approval of experiments.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intersecting Storage Rings Committee (ISRC), 1968 - 1983 |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1968 the ISR Experiments committee was set up with Jentschke as its Chairperson, five members from outside experimental groups, four members from CERN experimental groups and four members from the ISR Construction Departement. The ISRC's main task was to examine experimental proposals for the ISR and recommend a consistent experimental programme to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC). The first meeting of the ISRC was held on 13 January 1969. Unlike the Track Chamber Committee (TCC) and Electronic Experiments Committee (EEC), the ISR Committee was based on a machine rather than on a detector system. Following the example of the EEC, the ISRC held both open and restricted meeting. The former were devoted to the presentation and discussion of experiment proposals and progress reports on the programme. In the restricted meetings, the Committee decided on its recommendations to the NPRC. In 1976 the NPRC was replaced by the Research Board (RB). At the end of 1983 the ISR were closed down to liberate financial and manpower resources for the Large Electron Positron Collider (LEP) construction and ISR Committee held its last meeting on 27 January 1984.
|
||||||||||||||||||
Large Hadron Collider Committee (LHCC), 1992 - Today |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Large Hadron Collider Committee (LHCC) was set up after the March 1992 General Meeting on LHC Physics and Detectors (ECFA Towards the LHC experimental programme) where expressions of interest were presented for experiments on the LHC. The LHCC makes recommendations to the Research Board (RB). The LHCC also reviews the LHC Computing Grid (LCG) Project. The LHCC is responsible for reviewing the remaining detector R&D projects (RD39, RD42 and RD50) having taken over the role of the Detector Research and Development Committee (DRDC) in 1995.
LHCC Database - Boxes: K0823 to K0845 - LHCC documents from 1992 to 1999 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC), 1961 - 1975 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1960 the Director-General John Adams proposed a number of measures to define a global policy for the exploitation of the Synchro-Cyclotron and the new Proton Synchrotron. He decided to create three Committees, one for each experimental technique used:
The recommendations of these three committees were then passed to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC) under the Chairpersonship of the Director-General, which took the final decisions concerning the experimental programme and the facilities offered by the PS and SC accelerators. The NPRC took into consideration not only the scientific merit of the experiments proposed, but also their technical and financial implications and whether they were compatible with the other experiments in the programme.
The members of the NPRC were the chairmen of the Emc, TCC, EEC, and the leader, or a representative of the Nuclear Physics (NP), Theory (TH), Proton Synchrotron (PS), Synchro-Cyclotron (SC), Data Handling (DD), Track Chamber (TC) and Nuclear Physics Apparatus (NPA) divisions.
In addition to approving new proposals the Physics Committee and the NPRC regularly reviewed the status and needs of the various experiments in progress.
In 1976 (end of the bubble chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental techniques, and basing it instead on the machine. The NPRC was replaced by the Research Board (RB).
Source : CERN-344-Rev.4 ; CERN Courier, Vol.7, N°3
|
||||
Nuclear Structure Committee (NSC), 1964 - 1966 |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1964 Torleif Ericson, together with the head of CERN's NP division Peter Preiswerk, proposed that the Director-General create a Nuclear Structure Committee (NSC). This was set up soon after with Ericson as Chairperson. The aim of NSC was to discuss and to decide on experimental proposals in the field of nuclear structure research; and to provide some co-ordination between the groups inside and outside of CERN that took part in the nuclear structure programme at the Synchro-Cyclotron (SC). This committee met only seven time before it merged in 1966 with EmC and was renamed the Physics III Committee (PH-III-COM).
|
|||||||||||||
Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC), 1976 - 1978 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
In 1976 (end of the bubble chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental techniques, and basing it instead on the machine. The Electronic Experiments Committee (EEC) and Track Chamber Committee (TCC) (after 1966 commonly called the Physics I (PH-I-COM) and Physics II (PH-II-COM) Committees) merged to become the Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC). The PSC examined all experimental proposals for the 28 GeV Proton Synchrotron and made recommendations to the Research Board (RB). In 1978 the PSC and the Synchro-Cyclotron Experiment Committee (SCC) fused to form the Proton Synchrotron and Synchro-Cyclotron Committee (PSCC).
Source : History of CERN, Vol. II & III
|
|||
Proton Synchrotron and Synchro-Cyclotron Committee (PSCC), 1978 - 1990 |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1978 the Synchro-Cyclotron Committee (SCC) and Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC) fused into the PSCC to advise on research at both machines (PS & SC). When the SC was shut down in 1990, the management of matters concerning ISOLDE (which moved to the Booster at the PS) was transferred to the ISOLDE Committee (ISC), and management of Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) was transferred to the Super Proton Synchrotron Committee (SPSC). Source : History of CERN, Vol. II & III
|
|||||||||||||||
Research Board (RB), 1976 - Today |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1976 the Research Board (RB) took over from the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC). The Research Board receives recommendations from all the CERN Experimental Committees, and takes decisions on them. Once approved, the proposals become part of the CERN experimental programme. The Research Board also decides on the accelerator schedules and requests for "Recognized Experiments" at CERN.
|
|||||||||
Synchro-Cyclotron Commitee (SCC), 1976 - 1977 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
In 1976 (end of the Bubble Chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental techniques, and basing it instead on the machine. The Physics III Committee (PH-III-COM) was renamed the Synchro-Cyclotron Committee. The SCC examined all experimental proposals for the SC and made recommendations to the Research Board, which replaced the NPRC in 1976. In 1978 SCC and Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC) fused into the PS & SC Committee (PSCC) to advise on research at both machines (PS & SC).
Source : History of CERN, Vol. II & III
|
|||
Super Proton Synchrotron Committee (SPSC) - 1st Period, 1973 - 1990 |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1973 the Super Proton Synchrotron Experiments Committee (SPSC) was set up with Pierre Lehmann as its Chairperson. The SPSC examined all experimental proposals and made recommendations to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee (NPRC). In 1990 the management of the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) experiments was transferred to the SPSC which became the Super Proton Synchrotron and LEAR Committee (SPSLC).
|
||||||||||||||||||
Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) and Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR) Committee (SPSLC), 1990 - 1996 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1990 the Super Proton Synchrotron Committee (SPSC) was renamed SPS and LEAR committee (SPSLC) when it took over management of the LEAR experiment. The mandate of the committee was to referee requests from the experimental teams on the basis of their physics interest and of the availability of the accelerators. SPSLC recommendations were sent to the Research Board (RB) for final decision. The SPSLC met about five times a year. In 1997 with the end of LEAR, the SPSLC reverted to its former name SPSC.
|
||||||
Super Proton Synchrotron and Proton Synchrotron Committee (SPSC) - 2nd Period, 1997 - Today |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1997, with the end of the Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR), the Super Proton Synchrotron and LEAR Committee (SPSLC) retook his former name SPSC. The mandate of the committee is to referee requests from the experimental teams on the basis of their physics interest and of the availability of the accelerators. SPSC recommendations are sent to the Research Board (RB), which takes the decisions. The SPSC meets about five times a year.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Track Chamber Committee (TCC) - Physics II Committee (PH-II-COM), 1961 - 1976 |
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
In 1960 the Director-General John Adams proposed a number of measures to define a global policy for the exploitation of the new Proton Synchrotron. He decided to create three committees, one for each experimental technique used:
These three new committees were proposed to replace the Advisory Committee and Bubble Chamber Committee.
The TCC functions were to propose to the Nuclear Physics Research Committee track chamber experiments to be carried out at CERN, and also to form a link between the European track chamber groups and the CERN Laboratory.
The TCC came into operation in 1961, and met about once a month. It comprised a Chairperson (a senior physicist working on track chamber experiments, not on the staff of CERN) and members (representatives of CERN and other European track chamber groups (including picture evaluation groups)) wanting to use CERN facilities.
After 1966 the TCC was commonly known as the Physics II (PH-II-COM). It considered and selected the proposals for experiments using the bubble chambers at CERN :
In 1976 (end of the bubble chambers period) John Adams and Leon Van Hove rationalized the system, abolishing the committee system based on experimental technique, and basing it instead on the machine. EEC and TCC merged to become the Proton Synchrotron Committee (PSC).
Source : CERN-344-Rev.4 ; CERN Courier, Vol.7, N°3
|
||||||||||||||||||